Rebex SSH Shell
SSH shell, tunneling, telnet, ANSI terminal emulation library for .NET
Download 30-day free trial Buy from $999More .NET libraries
-
 Rebex SFTP
Rebex SFTP
SFTP client
-
 Rebex SSH Pack
Rebex SSH Pack
SSH Shell + SFTP + SSH server
-
 Rebex Total Pack
Rebex Total Pack
All Rebex .NET libraries together
Back to feature list...
Windows Forms terminal control
On this page:
More features:
- Powerful scripting API
- History buffer
- Palettes
- Color schemes
- Fonts
- Line drawings characters in all fonts
- Screen scraping
- Emulation of VT100, xterm, VT52 and other terminals
- Settings and options
- Remote exec
Terminal control for Windows Forms
TerminalControl is a terminal emulation control for Windows Forms applications.
It makes it very simple to add SSH and telnet terminal emulation capabilities to your .NET application for Windows.
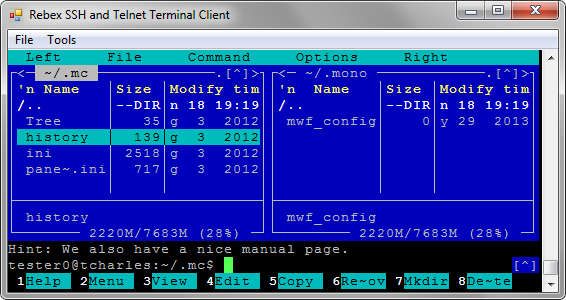
In addition to Winforms-specific features described on this page, TerminalControl shares
many additional features with VirtualTerminal.
The following code connects and authenticates to an SSH server and starts a terminal session:
// create an instance of SSH, connect and log in
ssh = new Ssh();
ssh.Connect(serverName);
ssh.Login(username, password);
// bind the TerminalControl object (that was added
// to the Form using Visual Studio designer) to the
// SSH channel (creates a SSH shell session)
this.Terminal.Bind(ssh);
' create an instance of SSH, connect and log in
Dim ssh As New Ssh()
ssh.Connect(serverName)
ssh.Login(username, password)
' bind the TerminalControl object (that was added
' to the Form using Visual Studio designer) to the
' SSH channel (creates an SSH shell session)
Me.Terminal.Bind(ssh)
Note: TerminalControl is only supported on Windows.
Note: Use Telnet object to connect and
authenticates to a telnet server.
Similarly, use SerialPortChannel object to communicate with devices connected over a serial port.
Customized text cursor - blinking and color
TerminalControl supports cursor blinking - just set CursorBlinkingInterval to a desired value (in miliseconds).
And if you prefer a different cursor color than the default green one, registed CursorColor event handler to set your own colors:
terminal.CursorColor += (sender, args) =>
{
// black text on yellow background
args.ForeColor = TerminalColor.Black;
args.BackColor = TerminalColor.Yellow;
};
AddHandler terminal.CursorColor,
Sub(sender, args)
' black text on yellow background
args.ForeColor = TerminalColor.Black
args.BackColor = TerminalColor.Yellow
End Sub
The CursorColor event is quite powerful - in addition to simply setting the desired color, you can derive it from the
original colors of the character cell:
terminal.CursorColor += (sender, args) =>
{
// invert original cell color
args.ForeColor = args.CellBackColor;
args.BackColor = args.CellForeColor;
};
AddHandler terminal.CursorColor,
Sub(sender, args)
' invert original cell color
args.ForeColor = args.CellBackColor
args.BackColor = args.CellForeColor
End Sub
Blinking cursor can be customized as well - use Blink event argument to determine the current blink state:
terminal.CursorColor += (sender, args) =>
{
if (args.Blink)
{
// black text on yellow background
args.ForeColor = TerminalColor.Black;
args.BackColor = TerminalColor.Yellow;
}
else
{
// cursor not visible
args.ForeColor = args.CellForeColor;
args.BackColor = args.CellBackColor;
}
};
AddHandler terminal.CursorColor,
Sub(sender, args)
If (args.Blink) Then
' black text on yellow background
args.ForeColor = TerminalColor.Black
args.BackColor = TerminalColor.Yellow
Else
' cursor not visible
args.ForeColor = args.CellForeColor
args.BackColor = args.CellBackColor
End If
End Sub
Selection and clipboard
TerminalControl supports various clipboard operations - mouse-based selection, copying and pasting.
Three different kinds of selections are available (character mode, whole-word mode and line mode) - use double-click or triple-click to activate them.
Block selection is supported as well (hold Ctrl character to enable it).
// changes the default selection mode to block mode
terminal.SelectionMode = TextSelectionMode.Block;
// specifies whether the right mouse button pastes text from clipboard
terminal.MousePasteEnabled = true;
// specifies whether selection a text using a mouse automatically copies the
// selected text into clipboard
terminal.MouseSelectionCopiesToClipboard = true;
' changes the default selection mode to block mode
terminal.SelectionMode = TextSelectionMode.Block
' specifies whether the right mouse button pastes text from clipboard
terminal.MousePasteEnabled = True
' specifies whether selection a text using a mouse automatically copies the
' selected text into clipboard
terminal.MouseSelectionCopiesToClipboard = True
Tip: Use SelectionChanged event to get notified when a selection is changed.
Text can be selected and retrieved programmatically as well:
// select the area starting at position 10, 8 and ending at 50, 12.
terminal.SetSelection(10, 8, 50, 12);
// retrieve the selected text
string text = terminal.GetSelectedText();
// unselect the selected area
terminal.ResetSelection();
' select the area starting at position 10, 8 and ending at 50, 12.
terminal.SetSelection(10, 8, 50, 12)
' retrieve the selected text
Dim text As String = terminal.GetSelectedText()
' unselect the selected area
terminal.ResetSelection()
Note: Don't forget to mark your application's entry point routine (Main) with [STAThread] attribute to enable clipboard functionality.
Scrolling and scroll bar
TerminalControl supports history buffer and provides a scroll bar
to view its contents. Mouse wheel can be used to scroll back and forth as well. Several aspects of scrolling behavior are configurable:
// when data is received, scroll to the currently visible screen
terminal.ScrollbackResetOnDisplayActivity = true;
// scroll back by 20 lines
terminal.Scroll(-20);
// disable scroll bar
terminal.ScrollBarEnabled = false;
// disable history buffer by setting its length to zero
terminal.HistoryMaxLength = 0;
' when data is received, scroll to the currently visible screen
terminal.ScrollbackResetOnDisplayActivity = True
' scroll back by 20 lines
terminal.Scroll(-20)
' disable scroll bar
terminal.ScrollBarEnabled = False
' disable history buffer by setting its length to zero
terminal.HistoryMaxLength = 0
Resizing
In most cases, you don't have to care about resizing - just select a font, specify a reasonable control size and most remote shells and the control and remote terminal applications will adjust automatically to utilize the new screen size.
However, if you need to use a specific screen size for some reason (such as a legacy terminal that only supports a fixed screen size), it's still rather simple:
// disable automatic terminal size adjustment based on font size and control size.
terminal.AutoAdjustTerminalSize = true;
// use a new font
terminal.TerminalFont = new TerminalFont(FontFamily.GenericMonospace, 12);
// determine the size of a single character cell
Size cellSize = terminal.CellSize;
// resize the terminal control to 80 character columns and 25 character rows
terminal.SetScreenSize(80, 25);
// or alternatively, if you need more control over the process...
// calculate a control size corresponding to the screen size
// of 80 character columns and 25 character rows
// (includes scroll bar width)
Size requiredSize = terminal.GetControlSize(80, 25);
// resize the terminal control
// (in practice, you would rather resize one of the parent controls)
terminal.Size = requiredSize;
' disable automatic terminal size adjustment based on font size and control size.
terminal.AutoAdjustTerminalSize = True
' use a new font
terminal.TerminalFont = New TerminalFont(FontFamily.GenericMonospace, 12)
' determine the size of a single character cell
Dim cellSize As Size = terminal.CellSize
' resize the terminal control to 80 character columns and 25 character rows
terminal.SetScreenSize(80, 25)
' or alternatively, if you need more control over the process...
' calculate a control size corresponding to the screen size
' of 80 character columns and 25 character rows
' (includes scroll bar width)
Dim requiredSize As Size = terminal.GetControlSize(80, 25)
' resize the terminal control
' (in practice, you would rather resize one of the parent controls)
terminal.Size = requiredSize
Tip: Prefer a terminal control that keeps a fixed screen size when resized and automatically changes the font size instead?
Although TerminalControl can't do this by default, it is possible with a bit of additional work -
check out FontResizableTerminalControl object's code.
Processing modes
By default, TerminalControl automatically receives and processes incoming data and updates the screen on-the-fly.
This is perfect when the control is used manually by a user. However, if you need to use the
scripting API to control
the terminal programmatically, this automatic data processing mode needs to be disabled first:
// disable automatic processing mode
terminal.SetDataProcessingMode(DataProcessingMode.None);
// you can use the scripting API now...
// detect prompt
terminal.Scripting.DetectPrompt();
// send a command
terminal.Scripting.SendCommand("uname -a");
// read its response
string result = terminal.Scripting.ReadUntilPrompt();
// enable automatic processing mode again
terminal.SetDataProcessingMode(DataProcessingMode.Automatic);
' disable automatic processing mode
terminal.SetDataProcessingMode(DataProcessingMode.None)
' you can use the scripting API now...
' detect prompt
terminal.Scripting.DetectPrompt()
' send a command
terminal.Scripting.SendCommand("uname -a")
' read its response
Dim result As String = terminal.Scripting.ReadUntilPrompt()
' enable automatic processing mode again
terminal.SetDataProcessingMode(DataProcessingMode.Automatic)
Key mapping and input modes
TerminalControl handles most commonly used key strokes, but new ones can be added without much work.
For example, to add support for Ctrl+arrow key combinations, just register the following KeyDown event handler:
// register a custom KeyDown event handler
terminal.KeyDown += (sender, e) =>
{
if (!e.Control)
return;
char code = ' ';
switch (e.KeyCode)
{
// detect Ctrl+arrow strokes
case Keys.Up: code = 'A'; break;
case Keys.Down: code = 'B'; break;
case Keys.Right: code = 'C'; break;
case Keys.Left: code = 'D'; break;
}
if (code != ' ')
{
// send the appropriate escape sequence
terminal.Scripting.Send("\x1B[1;5" + code);
e.Handled = true;
return;
}
};
' register a custom KeyDown event handler
AddHandler terminal.KeyDown,
Sub(sender, e)
If Not e.Control Then
Exit Sub
End If
Dim code As Char = " "c
Select Case e.KeyCode
' detect Ctrl+arrow strokes
Case Keys.Up
code = "A"c
Exit Select
Case Keys.Down
code = "B"c
Exit Select
Case Keys.Right
code = "C"c
Exit Select
Case Keys.Left
code = "D"c
Exit Select
End Select
If code <> " "c Then
' send the appropriate escape sequence
terminal.Scripting.Send(ChrW(27) & "[1;5" & code)
e.Handled = True
Exit Sub
End If
End Sub
It's also possible to disable any kind of user input (this is useful when you only control the remote terminal programmatically), or suppress default behavior of some key combinations:
// intercept Alt+key keystrokes and send them to the remote
// server instead of activating the application's menu
terminal.SuppressAltAsMenuKey = true;
// intercept shortcut keystrokes and send them
// to the remote server // instead
terminal.SuppressShortcutKeys = true;
// disable all user input
terminal.UserInputEnabled = false;
' intercept Alt+key keystrokes and send them to the remote
' server instead of activating the application's menu
terminal.SuppressAltAsMenuKey = True
' intercept shortcut keystrokes and send them
' to the remote server // instead
terminal.SuppressShortcutKeys = True
' disable all user input
terminal.UserInputEnabled = False
Back to feature list...
